Where Sand Meets Speed
Dive into the world of beach marathons, coastal athletics, and seaside fitness. From training guides to race coverage, we bring you everything you need to know about running by the ocean.
Explore Sports That Move You
From the court to the coast, discover comprehensive coverage across all disciplines
Basket
Basketball, NBA and competitions
Bike
Cycling, mountain biking and road
Bodybuilding
Bodybuilding, programs and nutrition
Combat
Boxing, MMA and martial arts
Fitness
Fitness, training and workouts
Football
Football, Premier League and leagues
News
Sports news and results
Other sports
Tennis, swimming and other sports
Latest articles
Our recent publications

Exploring the evolution of uk basketball infrastructure for enhanced growth support
Understanding the history of UK basketball infrastructure reveals a journey from modest beginnings to a more structured sporting environment. Initially, basketball in the UK depend...
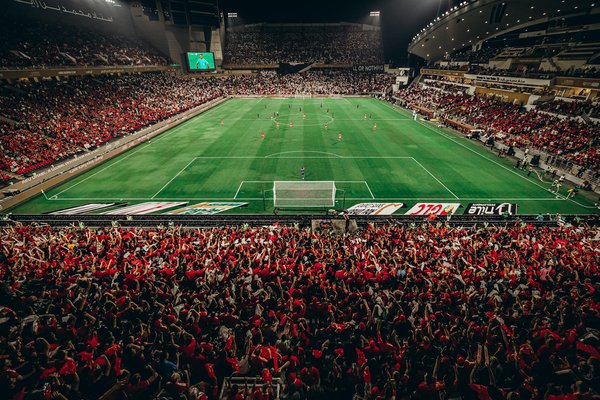

Exploring the rising popularity of basketball in the uk: what draws the crowd?

Unveiling the secret playbook: how uk basketball can achieve international glory
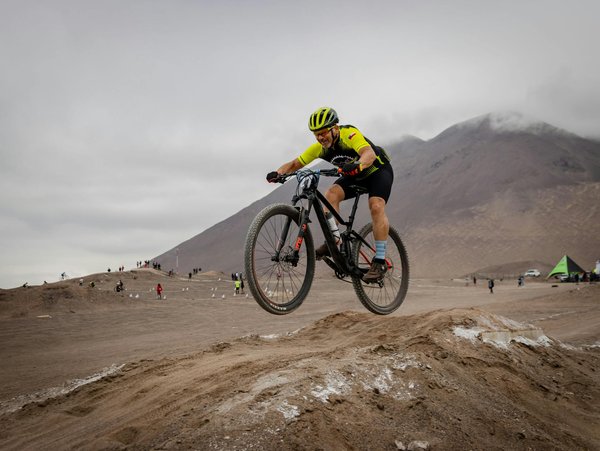

How can beginners start their sport biking journey in the UK?

How Can UK Cyclists Improve Their Endurance for Long Rides?

How Does Cycling Transform Urban Mobility in the UK?
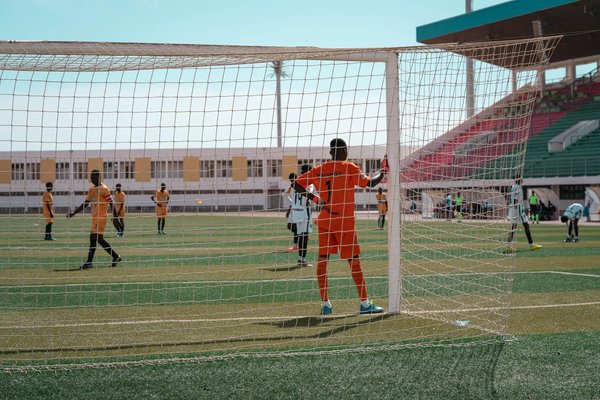

How Can UK Combat Sports Enthusiasts Improve Their Techniques?
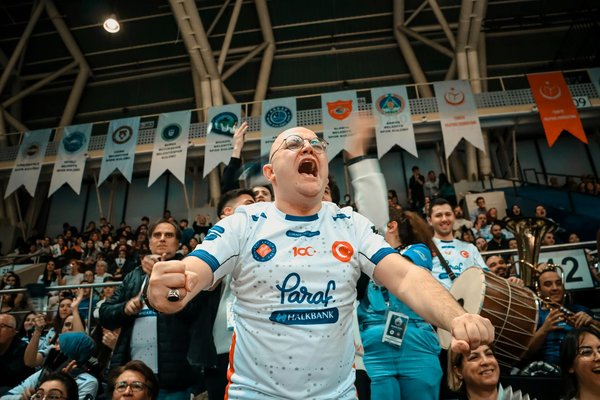

How Does Mental Resilience Affect Success in UK Combat Sports?

What New Innovations Are Shaping the Future of Combat Sports?

How can UK fitness challenges motivate personal growth?

Master top-tier footwork drills every squash lover needs for unmatched performance

What are the best UK sports venues for fitness enthusiasts?

How Can UK Football Culture Inspire Community Unity?

How Can We Improve Youth Engagement in UK Football?
How Can You Enhance Your Football Training Through British Football Legacy?

How Can Innovations in UK Sports News Reshape Its Future?

How Can Upcoming UK Sport Events Influence Community Engagement?

How Will Upcoming UK Sporting Events Impact Local Communities?

How are alternative sports impacting cultural diversity in the UK sports scene?

What are the challenges faced by female athletes in UK alternative sports?

What Are the Hidden Challenges in Less Recognized UK Sports?
Ready to Hit the Sand?
Explore our latest features, race analyses, and training resources to elevate your beach sports journey today.
Rejoindre →